Neurodiagnostic technologist schools in Georgia are a great way to learn more about the field and get started on your career. There are many different options available, so you can choose the program that best fits your needs.
The path to becoming a neurodiagnostic technologist is not always easy, but it is worth it. The demand for these professionals is expected to increase over the next ten years, and they make an average salary of $60,000 per year. It’s not hard to see why people choose this profession!
Neurodiagnostic technologists work with patients who have neurological disorders such as strokes or Alzheimer’s disease. They use many different tools and techniques to determine what caused them and how best to treat them. Their job often requires them to work long shifts in hospitals or other environments where there are many patients at once, so if this sounds like something that interests you then getting into school might be a good idea sooner rather than later!
You can get all the information you need on neurodiagnostic technologist schools in georgia neurodiagnostic technologist certificate program, online eeg certification program, accredited neurodiagnostic technology program, neurodiagnostic technologist certificate program online, neurodiagnostic technology institute, neurodiagnostic technologist programs colorado and other related post here on collegelearners.
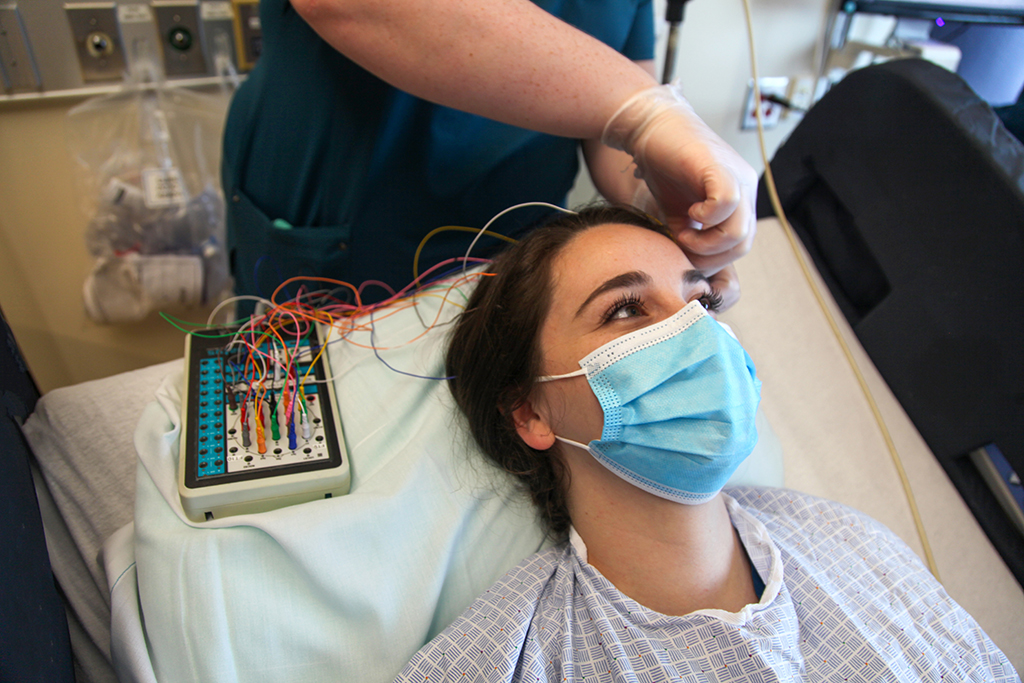
neurodiagnostic technologist certificate program
Have you ever wondered what’s going on in the brain of your friend? Or maybe you’re trying to figure out what’s wrong with your dad, who keeps getting lost on his way home. Well, if you want to know more about your brain, or someone else’s, then becoming a neurodiagnostic technician or technologist (NDT) might be right up your alley.
NDTs are the people who use sophisticated machinery to capture what’s going on in the brain. They can even take pictures of thoughts and brain patterns! This field is also referred to as electroneurodiagnostic (END) technology.
There are many different types of scans and tests that NDTs use in their work. One such test is called an electroencephalogram (EEG). The EEG measures electrical activity in the brain by measuring voltage fluctuations from electrodes placed on the scalp. These machines can track abnormal electrical activity in the brain caused by diseases like epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease.
Another test used by NDTs is called magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create images of organs inside your body without using x-rays or radiation exposure like CT scans do! MRI machines allow doctors to see things like tumors or damaged tissue inside brains without having.
Want to become a neurodiagnostic technologist? Do you have an interest in the human brain, and want to help people with neurological disorders? If so, there are several exciting professional opportunities available:
You can get started by enrolling in a two-year associate of applied science (AAS) degree program at a community college, or by completing an apprenticeship program. With either route, you’ll be able to work as a neurodiagnostic technologist after only two years of schooling—and many employers will pay for your education!
Once you’re in the field, there are several ways to further your career. You can pursue additional training and earn a certificate in sleep disorders, electroencephalogram (EEG) testing, or epilepsy. Or if you’re looking for even more independence from other professionals or organizations, consider becoming a certified professional member of the International Society for Clinical Neurophysiology (ISCN).
neurodiagnostic technologist schools in georgia
If you’re looking to get into the field of neurodiagnostic technology, Georgia is a great place to start. The state offers a number of different schools that offer programs in this fast-growing field. You can find an accredited school near you that will teach you everything you need to know about this exciting field.
Here are some of the best neurodiagnostic technologist schools in Georgia:
Georgia Institute of Technology: Atlanta, GA – This school offers an Associate’s degree in biomedical technology. Students will learn about anatomy and physiology, medical terminology, laboratory procedures and techniques, administrative tasks and ethics in biomedical science. The program also includes clinical rotations where students spend time at various hospitals learning about various diagnostic tests performed there.
Emory University: Atlanta, GA – This school offers a Bachelor’s degree in biomedical technology as well as an Associate’s degree in health science with a concentration in biomedical technology. Both programs include courses on anatomy and physiology with practical instruction on how they relate to current diagnostic tests used today by doctors around the world. Students will also learn about how these tests work so they can work effectively with other professionals who use them on a daily basis such as physicians or nurses who work directly with patients suffering from various
| School Name/Location | Program Name |
|---|---|
| Dalton State College Dalton, GA | Respiratory Therapy Technician/Assistant |
| Middle Georgia State University Macon, GA | Respiratory Therapy Technician/Assistant |
| Chattahoochee Technical College Marietta, GA | Electroneurodiagnostic/Electroencephalographic Technology/Technologist |

eeg tech certification
If you’re interested in a career as an EEG technician, it’s helpful to know the different certifications you can earn to help you be successful.
The first step is to get a high school diploma or equivalent. This will allow you to apply for an associate’s degree program at a community college or technical school. These programs typically last two years and award a certificate or diploma upon completion.
If you’re looking into earning an entry-level job as an EEG technician, it’s helpful to have at least some experience with EEG machines. You can gain this by completing a certification course through organizations like the American Society of Neuroradiology (ASNR). This training will teach you how to use and care for the equipment used in these jobs, such as computerized electroencephalography recording systems (CERs).
To advance your career as an EEG technician, consider getting certified through the American Board of Registration of Electroencephalographic Technologists (ABRET). This certification requires three years of work experience and passing an exam that tests your knowledge of EEG technology.
EEG certifications are professional credentials that show a neurodiagnostic technician has the skills and knowledge to operate EEG machines, which are medical devices that chart brainwaves to help physicians identify neurological, brain and sleep disorders. Many clinics and hospitals require their EEG technicians to receive a professional certification within a set time after their hiring date, such as one year. Most certifications require technicians to have a combination of education or work experience to be eligible for the exam. Technicians may also have to meet other requirements to earn a certification, such as basic life support or CPR training.
Benefits of earning EEG certifications
An EEG certification can help neurodiagnostic professionals show employers they have the skills to do their jobs effectively. Earning an EEG certification can help these technicians:
- Meet job requirements: If you’re looking to start a career in EEG technician, you may want to consider taking the Certified EEG Technician exam. Although it’s not required by employers, many employers may require their EEG technicians to become certified, so earning this credential can help you meet this requirement.
EEG technicians are responsible for monitoring patients who are undergoing surgery or experiencing other medical procedures that involve electrical stimulation of the brain. They use special equipment to monitor brain activity and make sure that treatments are working properly.
- Gain experience: Getting a certification can help EEG technicians gain experience in the field and learn skills to operate EEG machines and work with patients.
A certification may help you find employment as an EEG technician, but it is not required for all jobs. Some employers require their employees to have a certain amount of experience before they will consider them for a position, while others are willing to hire candidates without experience if they have certifications.
If you are looking for a job as an EEG technician, it is important to find out whether or not your potential employer requires a certification before deciding whether or not to pursue one.
- Demonstrate their competency: If you’re looking for a career in medical technology, you may want to consider getting an EEG certification. An EEG certification can show employers that a technician has demonstrated competency in this field.
The EEG technician is responsible for performing electroencephalography (EEG) tests and monitoring patients who have been diagnosed with brain disorders. This can include epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease and other neuropsychiatric disorders. The technician will perform these tests on patients in order to monitor their brain activity and determine if they are experiencing any issues or abnormalities.
An EEG technician may also be called upon to assist with other medical procedures that require anesthesia as well as monitor patient vital signs at all times during their stay at the hospital or medical facility where they work.
- Expand their job search: Having an EEG certification can make a technician eligible for more positions, which can expand their job search.
You’re ready to take the next step in your career as an EEG technician. You know that it’s important to have a certification, but you don’t know where to start. That’s why we’ve got you covered!
Our course is designed for students who are looking for a way to get their EEG certification quickly and affordably. We offer our course online so that you can work on it from anywhere in the world. You’ll learn everything you need to know about the process of becoming certified through our interactive lessons and quizzes, and you’ll get access to our experts if you ever have questions during your studies.
If you’re ready to take the next step in your career as an EEG technician, then this course is perfect for you!
- Advance their career: Earning additional certifications, such as an advanced certification for nervous system disorder testing, allows EEG technicians to learn new skills that can help them advance in their careers.
A certification from [company name] is the only way you’ll be able to become an advanced technician. Our program will teach you how to perform tests on patients who have nervous system disorders, including epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.
In addition to learning how to use the latest technology, like our state-of-the-art [product name], you’ll also get training in how to interpret results and communicate with other medical professionals.
Once you’ve completed this program and passed your certification exam, you’ll be ready to use your new skills in a variety of settings, including hospitals where patients are being treated for nervous system disorders.
Types of EEG certifications to earn
Those interested in becoming a certified EEG technician typically pursue credentials through the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Technologists (AAET) or the American Board of Registration for Electroencephalographic and Evoked Potential Technologists (ABRET).
The AAET offers two levels of certification: Registered EEG Technician (REGT) and Registered EEG/Evoked Potential Technologist (REEPT). Both require a combination of coursework, on-the-job training, and practical hands-on experience. The REGT requires at least one year’s worth of experience as an EEG technician before taking the exam to become certified; those who become REEPT must be licensed as an EEG technician before taking their exam.
The ABRET offers five levels of certification based on educational requirements, work experience, and examination results. Those who are interested should visit abret.org for more information about this organization’s certification process.
Here’s a look at seven certifications offered through these two highly recognized organizations:
1. Registered Nerve Conduction Study Technologist (R.NCS.T.)
The Registered Nerve Conduction Study Technologist (R.NCS.T.) certification is the only EEG credential offered by the AAET. Technicians can qualify for the certification under two pathways. The first requires one year of professional experience, while the second requires candidates to be a graduate of a neurodiagnostic technology program accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP). Under both pathways, candidates must show proof of 100 patient encounters or 30 continuing education credits through the AAET.
In addition to eligibility requirements, the AAET also requires technicians to submit a statement from their supervising physician that says they don’t perform invasive examinations or provide a copy of a superseding certificate that allows these procedures. If a candidate meets these requirements, they can apply to take the R.NCS.T. exam, which is a 250-question written test that evaluates a technician’s knowledge of physiology and anatomy, nerve conduction study principles and stimulation principles.
2. Registered Electroencephalographic Technologist (R. EEG T.)
The ABRET offers this certification for health care professionals who are practicing EEG technology. Technicians can become eligible for the certification through four pathways, which require candidates to be either:
- A graduate of a CAAHEP-accredited neurodiagnostic technology program with documentation of 50 EEGs and current basic life support (BLS) or CPR certifications
- A professional with a certificate of completion from an ABRET-recognized program with documentation of 100 EEGs and current BLS or CPR certifications
- A graduate with an associate degree or a Registered Polysomnographic Technologist (RPSGT) certification with one year of clinical EEG experience, documentation of 150 EEGs, 30 EEG credits through the Neurodiagnostic Society (ASET) and current BLS or CPR certifications
- A professional with four years of clinical EEG experience with documentation of 150 EEGs, 60 EEG credits through the ASET and current BLS or CPR certifications
If a candidate meets the requirements, they can apply to take the R. EEG T. exam, which comprises multiple-choice questions and takes about four hours to complete. The exam covers topics such as preparing patients, ensuring data integrity, identifying waveforms and providing analysis. Candidates who pass the exam earn the certification, which is valid for five years.
3. Certification in Neurophysiologic Intraoperative Monitoring (CNIM)
This ABRET certification is a good choice for technicians who have advanced knowledge of neurodiagnostic procedures. A technician can meet the requirements for this certification in one of four ways:
- Earning a CAAHEP diploma from a neurological intraoperative monitoring (NIOM) program with documentation of 100 NIOM cases and current BLS or CPR certifications
- Having a current R. EEG T. certification with documentation of 150 NIOM cases and current BLS or CPR certifications
- Having a bachelor’s degree with documentation of 150 NIOM cases, 30 educational hours and current BLS or CPR certifications
- Receiving a certificate of completion from an ABRET-recognized program and providing documentation of 150 NIOM cases and current BLS or CPR certifications
Candidates who meet these requirements can apply to take the exam, which is a four-hour test with multiple-choice questions. The exam evaluates a technician’s knowledge of fundamental neurological concepts, intraoperative phases and post-operative phases. Professionals who earn this certification can renew it every five years.
4. Certified Long-Term Monitoring Technologist (CLTM)
EEG technicians can earn this ABRET certification if they already have the R. EEG T. certification and at least one year of neurophysiological long-term monitoring experience following their EEG certification. The organization also requires candidates to provide proof of 50 long-term monitoring cases and their current BLS or CPR certifications. The exam for this certification includes questions on pre-study preparation, monitoring techniques and post-study procedures. Professionals can renew their CLTM certification after five years.
5. Certified Autonomic Professional (CAP)
The Certified Autonomic Professional (CAP certification) from ABRET is a good choice for technicians who have knowledge and experience with autonomic testing for nervous system disorders. Professionals can qualify for the certification under two pathways:
- An associate degree and one year of clinical autonomic testing experience with documentation of 20 autonomic cases, at least three autonomic-related educational activities in the past three years and current BLS or CPR certifications
- Two years of clinical autonomic testing experience with documentation of 40 autonomic cases, a minimum of three autonomic-related educational activities within the last three years and current BLS or CPR certifications
Candidates for the CAP certification also take a four-hour exam with multiple-choice questions. The exam evaluates the professional’s knowledge of patient assessment, preparation, patient tests and testing factors. The certification is valid for five years.
6. Certification for Magnetoencephalography Technologists (CMEG)
This ABRET certification requires technicians to have their R. EEG T. credential, at least six months of supervised experience, documentation of 25 evoked cases or 50 spontaneous cases and current BLS or CPR certifications. Candidates for this certification complete 12 modules and quizzes before taking the final proctored exam. The modules cover various areas, including the helium transfer process, basic magnetoencephalography principles and data acquisition. Candidates must achieve passing scores of 80% or higher on all module quizzes before taking the final exam. Professionals with this certification can renew it every five years by completing 15 hours of continuing education.
7. Certificate in NeuroAnalyst-CLTM (NA-CLTM)
This ABRET certification is for technicians who have at least one year of experience with neurophysiological long-term monitoring. Candidates can meet eligibility requirements for the certification in two ways:
- Having a bachelor’s degree and two years of experience as a CLTM technologist with documentation of 50 technical reports and 30 advanced long-term monitoring continuing education credits
- Having three years of experience as a CLTM technologist with documentation of 50 technical reports and 50 advanced long-term monitoring continuing education credits
Technicians who meet the requirements can apply to take the exam, which tests their knowledge of case presentations and EEG patterns. The exam covers topics such as recording parameters, seizure semiology and electrographic findings. The NA-CLTM certification is valid for five years.
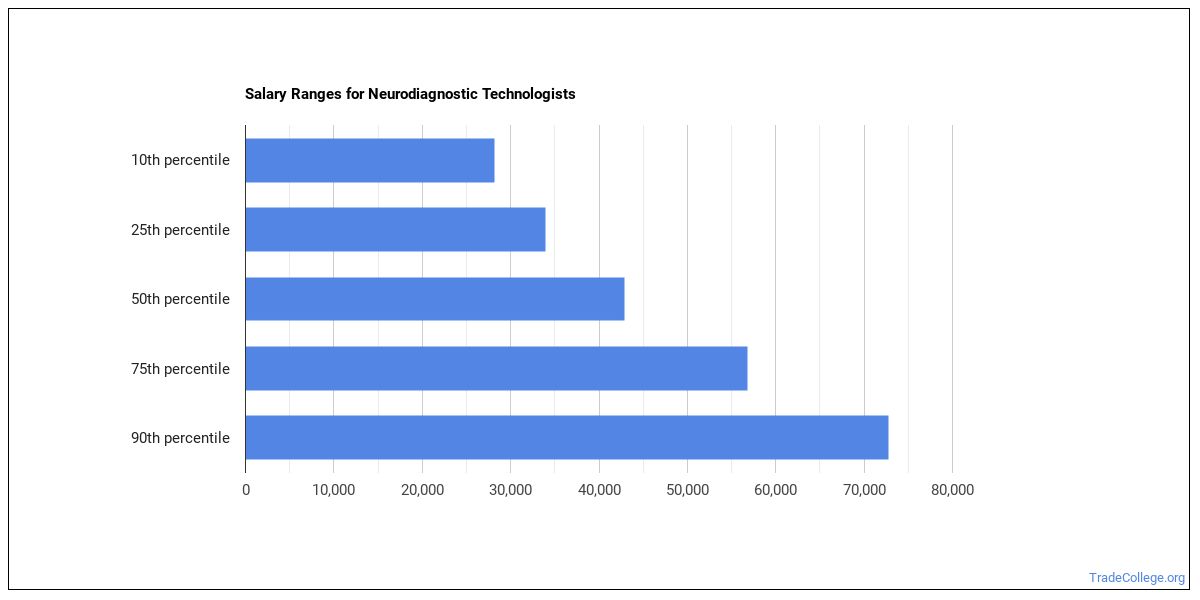
neurodiagnostic technologist salary
Are you a Neurodiagnostic Technologist? If so, then you’re likely to earn an average of $63,399 a year. That’s not bad—but it could be better!
The bottom 10% of Neurodiagnostic Technologists make just $33,000 a year, while the top 10% make about $118,000.
If you want to earn more than the average salary for your profession—and who doesn’t?—then there are some things you can do to help boost your pay. First off: negotiate. You might not get as much as another person with similar experience and education, but if you don’t ask for what you want, then you’ll never get it—so why not try? You may be surprised at how much more comfortable talking about money can make you feel once you start doing it.
Another way to boost your income is by getting additional training. Your employer may offer courses or seminars on a regular basis that will help prepare you for new responsibilities within your field or teach you something new that can be applied in your job. If they don’t provide such opportunities, then look into taking some classes yourself through an online platform like Coursera or Udemy so that when an opportunity.
Neurodiagnostic Technologist Salary By Year
Leave a Reply